Exercise 2: Importing Weather Station Data using the Synoptic API
This Notebook demonstrates how to query the Synoptic API using httr2.
The desired output is a table containing:
-
daily minimum and maximum air temperature
- one weather station ( CIMIS Station 077 (Oakville) )
- the current growing season (Jan 1st thru yesterday)
The table should have the following columns:
-
loc_id: location id (we’ll use the Synoptic station ID for CIMIS station 077, “CI077”) -
period: ‘rp’ (recent past)
-
date: date
-
tasmin: minimum daily temperature
-
tasmax: maximum daily temperature
1 Read about Synotic’s data and API
The first step in using any API is to read about the organization, the data, and tht API documentation.
Highlights of Synoptic:
Synoptic aggregates and redistributes data from weather station networks all over the world
every station has a unique ID
data are provided hourly
a public token is required to make calls to the API
2 Gather all the information needed to query the API
Sign-up for account and create a public token.
-
Find the Station ID of your station of interest:
Start here: https://viewer.synopticdata.com/
Check data availability: https://availability.synopticdata.com/
-
Determine which end point you need:
-
Read the docs for the end point
https://docs.synopticdata.com/services/time-series
Make a list of the search parameters you need
A good way to construct a test search is using the Synoptic Weather Query API Builder:
3 Create the API request object
Our work horse for calling APIs is httr2.
Define the base URL:
synoptic_ts_baseurl <- "https://api.synopticdata.com/v2/stations/timeseries"Create a variable with your Synoptic public token:
Define the Station ID (for this exercise we are using CI077 (Oakville CIMIS Station):
station_id_chr <- "CI077"Define the start time (midnight on January 1st):
library(lubridate) |> suppressPackageStartupMessages()
start_local_dt <- make_datetime(year = 2024, month = 1, day = 1,
hour = 0, min = 0, sec = 0,
tz = "America/Los_Angeles")
start_local_dt[1] "2024-01-01 PST"Convert the start time i) to UTC, then ii) to a character:
[1] "202401010800"For the end time, we will use 11pm yesterday:
yesterday_11pm_pdt_dt <- lubridate::as_datetime(Sys.Date() - 1, tz = "America/Los_Angeles") +
hours(23)
yesterday_11pm_pdt_dt[1] "2024-05-21 23:00:00 PDT"Convert the end time i) to UTC, then ii) to a character:
[1] "202405220600"Construct an object for the weather variables needed (see https://demos.synopticdata.com/variables/):
weather_vars <- "air_temp"We now have everything we need to create a request object!
4 Create the request object
stn_tas_req <- request(synoptic_ts_baseurl) |>
req_headers("Accept" = "application/json") |>
req_url_query(token = my_token,
start = start_utc_chr,
end = end_utc_chr,
stid = station_id_chr,
vars = weather_vars,
units = "english",
obtimezone = "local",
.multi = "comma")
stn_tas_req<httr2_request>GET
https://api.synopticdata.com/v2/stations/timeseries?token=91b8e95d3af4443aa981b43d25be7e06%20&start=202401010800&end=202405220600&stid=CI077&vars=air_temp&units=english&obtimezone=localHeaders:• Accept: 'application/json'Body: empty5 Call the API
See what will be sent when we send the request:
stn_tas_req |> req_dry_run() GET /v2/stations/timeseries?token=91b8e95d3af4443aa981b43d25be7e06%20&start=202401010800&end=202405220600&stid=CI077&vars=air_temp&units=english&obtimezone=local HTTP/1.1
Host: api.synopticdata.com
User-Agent: httr2/1.0.1 r-curl/5.2.1 libcurl/8.3.0
Accept-Encoding: deflate, gzip
Accept: application/jsonSend the request:
# Load a cached copy
stn_tas_resp <- readRDS(here::here("exercises/cached_api_responses/ex02_stn_tas_resp.Rds"))
# If you really want to send the request, uncomment the following:
# stn_tas_resp <- stn_tas_req |> req_perform()
# saveRDS(stn_tas_resp, file = here::here("exercises/cached_api_responses/ex02_stn_tas_resp.Rds"))
## Look at the response
stn_tas_resp<httr2_response>GET
https://api.synopticdata.com/v2/stations/timeseries?token=91b8e95d3af4443aa981b43d25be7e06%20&start=202401010800&end=202405220600&stid=CI077&vars=air_temp&units=english&obtimezone=localStatus: 200 OKContent-Type: application/jsonBody: In memory (76161 bytes)Check the status:
6 CHALLENGE #1
Create an API request object that asks for the temperature values in Celsius. Solution
## Your answer here6.1 Process the response
6.1.1 Convert the body to a list
Step 1 to process the response body is to extract it as a list:
stn_tas_lst <- stn_tas_resp |> resp_body_json()View the structure of the list:
A good way to explore the structure of the body is to open it in a View window:
# stn_tas_lst |> View()str(stn_tas_lst, max.level = 3)List of 4
$ STATION :List of 1
..$ :List of 17
.. ..$ ID : chr "8351"
.. ..$ STID : chr "CI077"
.. ..$ NAME : chr "Oakville"
.. ..$ ELEVATION : chr "190.0"
.. ..$ LATITUDE : chr "38.434"
.. ..$ LONGITUDE : chr "-122.410"
.. ..$ STATUS : chr "ACTIVE"
.. ..$ MNET_ID : chr "66"
.. ..$ STATE : chr "CA"
.. ..$ TIMEZONE : chr "America/Los_Angeles"
.. ..$ ELEV_DEM : chr "170.6"
.. ..$ PERIOD_OF_RECORD:List of 2
.. ..$ UNITS :List of 2
.. ..$ SENSOR_VARIABLES:List of 1
.. ..$ OBSERVATIONS :List of 2
.. ..$ QC_FLAGGED : logi FALSE
.. ..$ RESTRICTED : logi FALSE
$ SUMMARY :List of 9
..$ NUMBER_OF_OBJECTS : int 1
..$ RESPONSE_CODE : int 1
..$ RESPONSE_MESSAGE : chr "OK"
..$ METADATA_RESPONSE_TIME: chr "105.5 ms"
..$ DATA_QUERY_TIME : chr "34.3 ms"
..$ QC_QUERY_TIME : chr "52.6 ms"
..$ DATA_PARSING_TIME : chr "26.7 ms"
..$ TOTAL_DATA_TIME : chr "113.7 ms"
..$ VERSION : chr "v2.24.3"
$ QC_SUMMARY:List of 3
..$ QC_CHECKS_APPLIED :List of 1
.. ..$ : chr "sl_range_check"
..$ TOTAL_OBSERVATIONS_FLAGGED : int 0
..$ PERCENT_OF_TOTAL_OBSERVATIONS_FLAGGED: num 0
$ UNITS :List of 3
..$ position : chr "ft"
..$ elevation: chr "ft"
..$ air_temp : chr "Fahrenheit"6.1.2 Extract vectors of data for the data frame
Get the number of stations requested:
stn_tas_lst$SUMMARY$NUMBER_OF_OBJECTS[1] 1Extract the name of the ith station :
i <- 1
stn_tas_stationdata <- stn_tas_lst$STATION[[i]]
(stid_chr <- stn_tas_stationdata$STID)[1] "CI077"Extract the date-times:
obs_dt <- stn_tas_stationdata$OBSERVATIONS$date_time |>
unlist() |>
ymd_hms(tz = "America/Los_Angeles")Date in ISO8601 format; converting timezone from UTC to "America/Los_Angeles".## Inspect the vector:
class(obs_dt)[1] "POSIXct" "POSIXt" length(obs_dt)[1] 2351head(obs_dt)[1] "2024-01-01 00:00:00 PST" "2024-01-01 01:00:00 PST"
[3] "2024-01-01 02:00:00 PST" "2024-01-01 03:00:00 PST"
[5] "2024-01-01 04:00:00 PST" "2024-01-01 05:00:00 PST"range(obs_dt)[1] "2024-01-01 00:00:00 PST" "2024-05-21 23:00:00 PDT"Extract the hourly temperatures:
6.1.3 Create a tibble with the required structure
Bring them all together in a tibble. For this, we’ll want to use dplyr:
library(dplyr) |> suppressPackageStartupMessages()
# Set preferences for functions with common names
library(conflicted)
conflict_prefer("filter", "dplyr", quiet = TRUE)
conflict_prefer("count", "dplyr", quiet = TRUE)
conflict_prefer("select", "dplyr", quiet = TRUE)
conflict_prefer("arrange", "dplyr", quiet = TRUE)# View(stn_hrly_tbl)Convert from hourly to daily data:
Inspect the results:
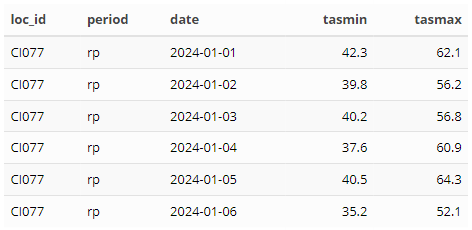
stn_dlytas_tblFinish-up to get the final format:
loc_id | period | date | tasmin | tasmax
stn_rctpast_dlytas_tbl <- stn_dlytas_tbl |>
mutate(period = "rp") |>
select(loc_id = stid, period, date, tasmin, tasmax)
head(stn_rctpast_dlytas_tbl)# View(stn_rctpast_dlytas_tbl)6.1.4 Save results
Save the final table to disk so we can open it in other exercises:
7 HOMEWORK
Bundle up this code in a function that returns a tibble of daily minimum and maximum temperature for any station in Synoptic. The function should cache the results in temp space for the current R session, which it should check first before calling the API.
syn_dailytas <- function(stid, start_dt, end_dt, token, cache = TRUE) {
## Insert your answer here
}